In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of treadmill speed sensors and uncover their inner workings. Delving into the intricacies of this crucial component, we will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how these sensors operate. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, a gym owner, or simply curious about the technology behind treadmills, this article will shed light on the mechanics behind the scenes and give you a glimpse into the mechanisms that help track your speed on these popular workout machines. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery together and uncover the secrets of how a treadmill speed sensor works.
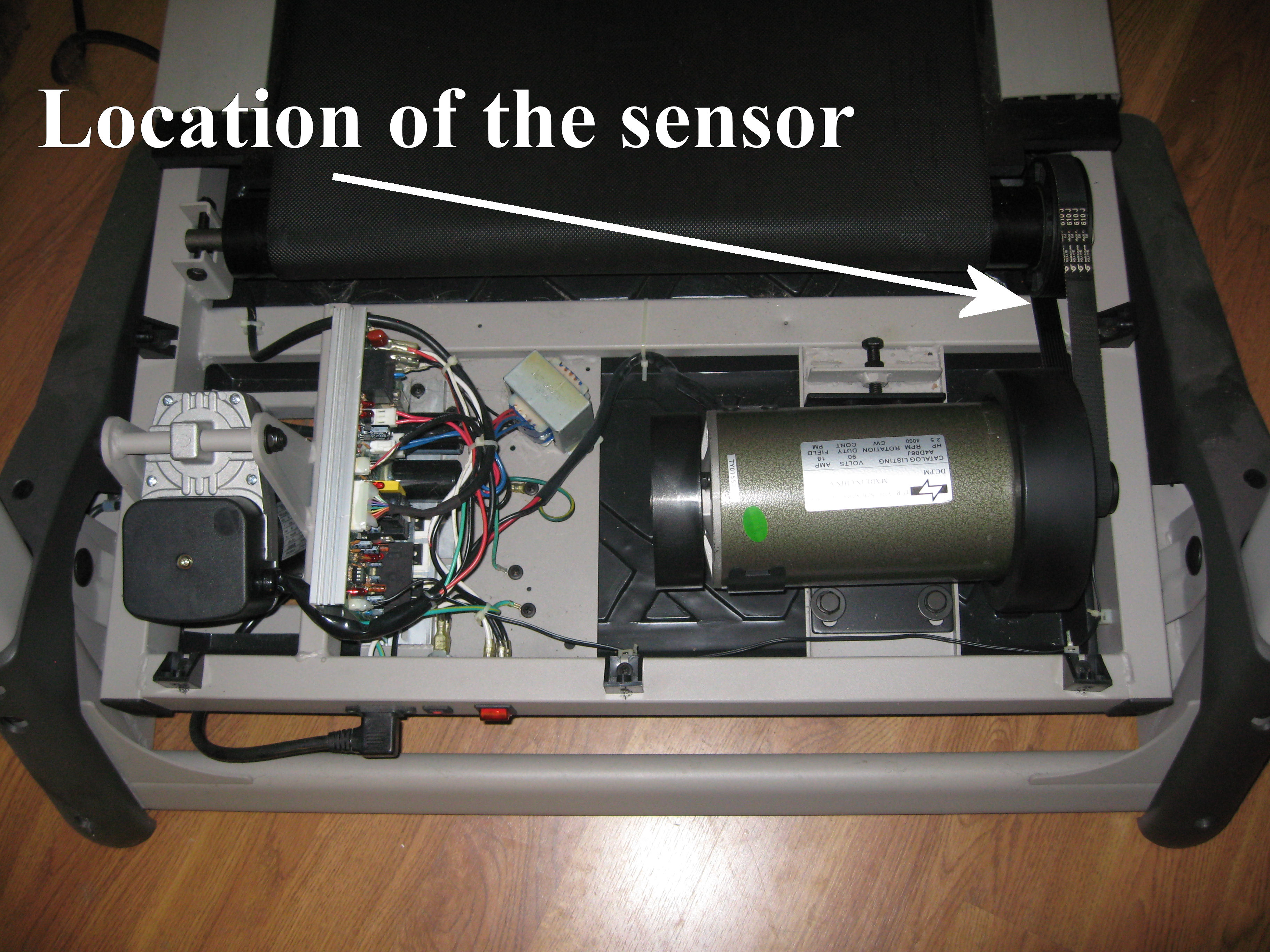
This image is property of www.wolfswords.com.
Overview of Treadmill Speed Sensor
A treadmill speed sensor is an essential component of a treadmill that measures and detects the speed of the belt or the movement of the user. It plays a critical role in ensuring accurate speed readings, which are crucial for monitoring and controlling the treadmill’s performance. By accurately measuring the speed, the speed sensor helps in maintaining the desired pace and providing valuable feedback to fitness enthusiasts and manufacturers. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the definition, importance, components, mechanism, types, and applications of treadmill speed sensors.
Definition of a Treadmill Speed Sensor
A treadmill speed sensor is a device that measures and detects the speed of the treadmill belt or the user’s movement on the treadmill. It consists of various components, such as sensors, magnets, light sources, and signal processing circuits, which work together to provide accurate speed readings. The speed sensor is usually located near the front roller or beneath the belt of the treadmill. It captures the rotational speed of the belt or the movement of the user’s feet and converts it into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the treadmill’s control system.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Importance of Treadmill Speed Sensor
The treadmill speed sensor is of utmost importance in the functionality and performance of the treadmill. It enables precise speed measurement, which is crucial for controlling the treadmill’s speed and maintaining the desired pace. Whether it’s for a casual walk, a challenging run, or interval training, accurate speed readings ensure that users can achieve their fitness goals effectively. Additionally, speed sensors provide valuable feedback to fitness enthusiasts, allowing them to track their progress, monitor their performance, and make necessary adjustments to their workouts. For manufacturers, speed sensors are essential in ensuring the safety, reliability, and overall quality of their treadmill models.
Components of a Treadmill Speed Sensor
A treadmill speed sensor is comprised of various components that work together to detect and measure the speed of the treadmill belt or the user’s movement. These components include:
-
Sensors: The sensors are responsible for detecting the motion or rotation of the treadmill belt or the user’s feet. They can be of different types, such as magnetic sensors or optical sensors, which we will discuss in detail later.
-
Magnets: In magnetic speed sensors, magnets are used to generate a magnetic field, which interacts with the sensor to produce a signal. These magnets are usually placed on the front roller or the pulley of the treadmill.
-
Light Sources: In optical speed sensors, light sources, such as infrared LEDs, are used to emit a beam of light towards a reflective surface. The reflection of this light is then detected by the sensor, enabling speed measurement.
-
Signal Processing Circuits: The electrical signals generated by the sensors or light sources need to be processed and interpreted by the treadmill’s control system. Signal processing circuits play a vital role in amplifying, filtering, and converting these signals into usable speed data.
By understanding the components of a treadmill speed sensor, we can delve deeper into its mechanism and explore the different types of sensors used in treadmills.
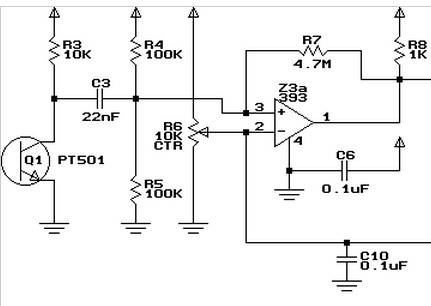
This image is property of i.stack.imgur.com.
Mechanism of Treadmill Speed Sensor
Understanding the mechanism of a treadmill speed sensor involves exploring the different types of sensors commonly used in treadmills – Hall effect sensors, magnetic speed sensors, and optical speed sensors. Each type operates differently and has its own advantages and limitations.
Types of Treadmill Speed Sensors
- Hall Effect Technology:
Hall effect sensors rely on the principle of the Hall effect to measure the speed of a treadmill. These sensors utilize a semiconductor device that detects changes in magnetic fields. When a magnetic field is applied perpendicularly to the flow of current in the device, it creates a measurable voltage output, which is proportional to the speed.
- Magnetic Speed Sensors:
Magnetic speed sensors use magnets and sensors to measure the speed of the treadmill. Typically, a magnet is attached to the front roller or the pulley of the treadmill. As the treadmill belt moves, the magnet rotates, generating a magnetic field. The sensor detects the changes in this magnetic field and converts it into electrical signals that can be used to determine the speed.
- Optical Speed Sensors:
Optical speed sensors employ light beams and reflective surfaces to measure the speed of the treadmill. A light source, usually an infrared LED, emits a beam of light towards a reflective surface, such as a strip on the treadmill belt or the user’s feet. The reflected light is then captured by a sensor, and the time taken for the reflection to reach the sensor is used to calculate the speed.
By utilizing these different types of sensors, treadmills are able to accurately measure speed and provide users with valuable data to enhance their workouts. Let’s explore each type in more detail.
Applying Hall Effect Technology
The Hall effect is a phenomenon that occurs when a magnetic field is applied to a conductor, resulting in a measurable voltage output. In the context of speed sensors, Hall effect technology utilizes this principle to measure the speed of a treadmill. A Hall effect sensor, which is a semiconductor device with three terminals, is employed to detect changes in the magnetic field generated by a magnet attached to the treadmill.
When the treadmill is in motion, the magnet rotates, causing a change in the magnetic field. This change is detected by the Hall effect sensor, which produces a voltage output that is proportional to the speed of the treadmill. The voltage output can then be interpreted by the treadmill’s control system to accurately determine the speed.
Hall effect technology offers several advantages in treadmill speed sensors. It provides reliable and accurate speed measurements, even at low speeds. Additionally, it is not affected by dust, dirt, or other environmental factors that may hinder the performance of other sensor types. This makes Hall effect sensors suitable for various treadmill applications, ranging from home treadmills to commercial gym equipment.
Magnetic Speed Sensors
Magnetic speed sensors utilize the interaction between magnets and sensors to measure the speed of a treadmill. In this type of sensor, a magnet is attached to the front roller or the pulley of the treadmill. As the treadmill belt moves, the magnet rotates, creating changes in the magnetic field. These changes are then detected by the sensor, which converts them into electrical signals for speed calculation.
Working Principle of Magnetic Speed Sensors
The working principle of magnetic speed sensors is based on the detection of magnetic field changes. As the magnet rotates, it generates a varying magnetic field. The sensor, typically a Hall effect sensor, measures the changes in this magnetic field and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed and interpreted to determine the speed of the treadmill.
Installation and Positioning of Magnetic Sensors in Treadmills
To ensure accurate speed readings, magnetic speed sensors need to be properly installed and positioned in treadmills. The magnet should be securely attached to the front roller or the pulley, allowing it to rotate freely without any obstructions. The sensor should be positioned in close proximity to the rotating magnet, ensuring that it can effectively detect the changes in the magnetic field.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Magnetic Speed Sensors
Magnetic speed sensors offer several advantages in treadmill applications. They provide reliable and accurate speed measurements, making them suitable for various fitness routines and training programs. Additionally, they are not affected by ambient light conditions, making them more reliable than optical sensors in certain environments.
However, magnetic speed sensors do have some limitations. They may require occasional maintenance, such as cleaning the magnet and sensor, to ensure optimal performance. Moreover, magnetic speed sensors may be susceptible to interference from nearby magnetic fields, which can affect their accuracy. Overall, careful installation and regular maintenance are necessary to maximize the performance and longevity of magnetic speed sensors.
Optical Speed Sensors
Optical speed sensors utilize light beams and reflective surfaces to measure the speed of a treadmill. These sensors rely on the principle of light beam reflection, where a beam of light is emitted towards a reflective surface, such as a strip on the treadmill belt or the user’s feet. The reflected light is then captured by a sensor, enabling speed measurement.
Understanding Optical Speed Sensors
Optical speed sensors work by emitting a beam of light towards a reflective surface. This surface can be a strip on the treadmill belt or a reflective material attached to the user’s shoes or feet. The light beam reflects off the surface and returns to the sensor, which measures the time it takes for the reflection to reach the sensor.
By calculating the time taken for the reflection, the optical speed sensor can determine the speed of the treadmill. This calculation is based on the known distance between the sensor and the reflective surface, allowing for accurate speed measurements.
Light Beam Reflection for Speed Measurement
The reflection of the light beam is a critical aspect of optical speed sensors. It is necessary for the reflective surface to have a sufficient amount of reflectiveness to ensure proper light beam reflection. Factors such as the surface material, cleanliness, and lighting conditions can affect the efficiency of the reflection. Therefore, regular cleaning and maintenance of the reflective surface are essential for accurate speed readings.
Benefits and Limitations of Optical Speed Sensors
Optical speed sensors offer several benefits in treadmill applications. They provide accurate and reliable speed measurements, even at high speeds. Additionally, they are not affected by magnetic fields, making them immune to interference from nearby equipment or magnetic objects. Optical speed sensors also offer versatility in terms of positioning, as they can be mounted at various locations on the treadmill.
However, optical speed sensors come with certain limitations. They may be affected by ambient light conditions, such as intense sunlight or bright artificial lighting, which can interfere with the light beam reflection. Regular cleaning of the reflective surface is necessary to maintain optimal performance. Furthermore, optical speed sensors may require periodic calibration to ensure accurate speed readings. Proper installation, maintenance, and calibration are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of optical speed sensors.
Signal Processing in Treadmill Speed Sensors
Signal processing plays a crucial role in treadmill speed sensors as it involves the detection, amplification, interpretation, and utilization of sensor data. The electrical signals generated by sensors need to be processed and converted into usable speed information. Let’s delve deeper into the signal processing aspects of treadmill speed sensors.
Signal Detection and Amplification
The initial step in signal processing is the detection and amplification of the electrical signals generated by the speed sensors. These signals may be very weak, especially in the case of optical speed sensors, which rely on the reflection of light. Signal amplification circuits are employed to increase the strength of these signals, ensuring they can be accurately interpreted by the treadmill’s control system.
Signal detection circuits use various techniques, such as amplifiers, filters, and noise reduction algorithms, to enhance the quality of the sensor signals. Amplifiers increase the amplitude of the signals, making them easier to detect and analyze. Filters eliminate unwanted noise and interference that may be present in the signals, improving the overall accuracy of the speed measurements.
By ensuring proper signal detection and amplification, treadmill speed sensors can provide reliable and precise speed data, facilitating effective treadmill usage and monitoring.
Interpretation of Sensor Data
Once the sensor signals are detected and amplified, they need to be interpreted to determine the speed of the treadmill. The interpretation of sensor data involves calculations and algorithms that convert the raw electrical signals into meaningful speed measurements.
Different types of sensors require distinct interpretation methods. For example, in Hall effect sensors, the voltage output is directly proportional to the speed of the treadmill, allowing for easy interpretation. In contrast, optical speed sensors require time-based calculations to measure the speed accurately.
The interpretation of sensor data is typically performed by microprocessors or dedicated signal processing circuits within the treadmill’s control system. These systems employ algorithms and calibration techniques to convert the sensor signals into usable speed information, which can be displayed on the treadmill’s console or transmitted to other devices for further analysis.
Incorporating Speed Feedback for Control
Speed sensors provide valuable feedback that can be used for controlling and adjusting the treadmill’s performance. By continuously monitoring the speed, the treadmill’s control system can make real-time adjustments to maintain the desired pace, provide accurate distance measurements, and facilitate various workout programs.
Speed feedback is essential for maintaining the speed consistency of the treadmill. It ensures that the belt moves at the desired pace, whether it’s for a leisurely walk, a steady jog, or an intense sprint. By receiving speed feedback from the sensors, the control system can adjust the motor’s output and belt tension to match the desired speed, allowing users to engage in effective and efficient workouts.
The incorporation of speed feedback in treadmill control systems enhances user experience, safety, and performance. It enables precise speed control, prevents sudden speed changes, and ensures smooth transitions between different speed levels and incline settings.
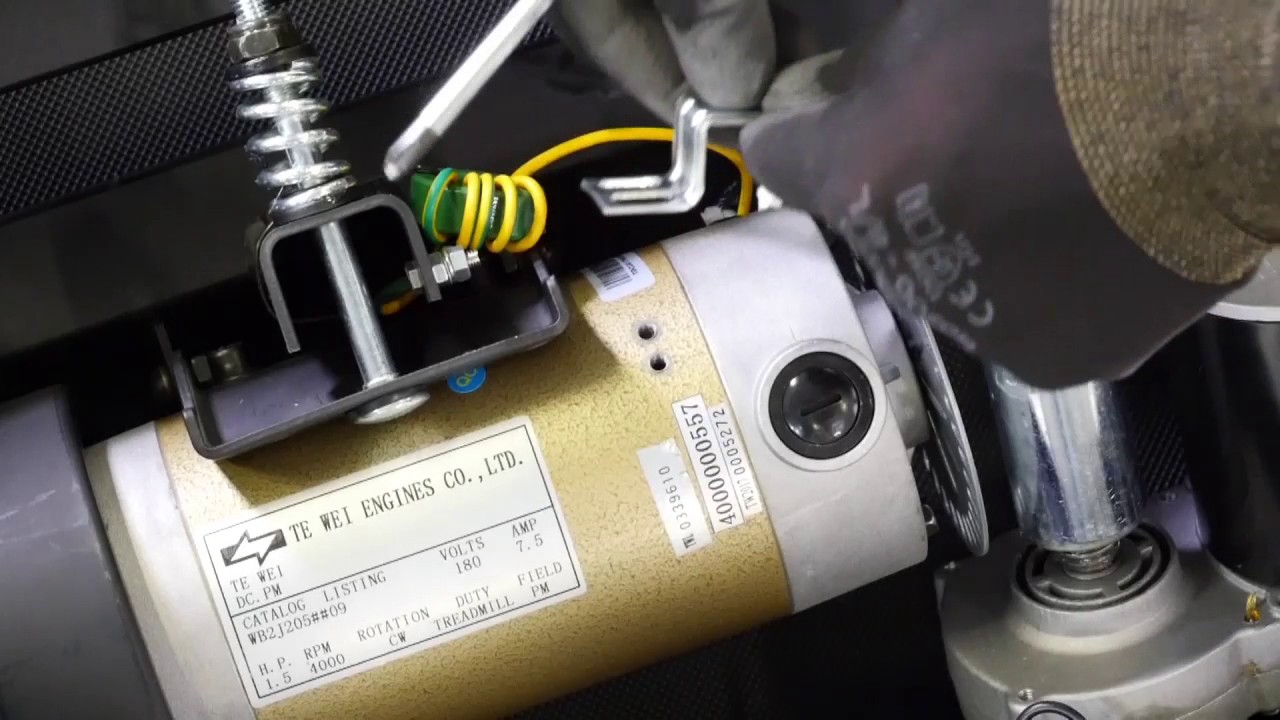
This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Calibration and Accuracy of Treadmill Speed Sensors
To ensure accurate and reliable speed measurements, treadmill speed sensors require calibration. Calibration involves adjusting and aligning the sensor system to accurately measure speed, taking into account factors that may affect measurement accuracy. Let’s explore the importance of calibration, calibration techniques, and factors that can impact sensor accuracy.
Importance of Calibrating Speed Sensors
Calibration is crucial for maintaining the accuracy and precision of treadmill speed sensors. Over time, the performance of sensors may change due to factors such as temperature variations, wear and tear, or manufacturing tolerances. Calibration helps bring the sensor’s measurements back to the desired accuracy, ensuring consistent and reliable speed readings.
Calibration also accounts for individual treadmill variations. Each treadmill model may have different belt dimensions, roller sizes, and motor characteristics, which can affect the speed measurement. By calibrating the speed sensor to the specific treadmill model, accurate speed readings can be achieved, regardless of these variations.
Calibration Techniques for Treadmill Speed Sensors
There are various calibration techniques employed for treadmill speed sensors, depending on the type of sensor and the specific treadmill model. Here are some common calibration techniques:
-
Manual Calibration: Some treadmills provide manual calibration options, where users can input known distances or speeds to calibrate the speed sensor. This method allows users to fine-tune the speed sensor’s accuracy based on their personal preferences or needs.
-
Auto Calibration: Many modern treadmills feature built-in auto calibration systems. These systems utilize algorithms and preset calibration routines to automatically adjust the speed sensors and ensure accurate speed measurements. Auto calibration may involve a series of speed and distance tests, during which the treadmill compares its actual output with the desired values and adjusts the speed sensor accordingly.
-
Manufacturer Calibration: Treadmill manufacturers often calibrate the speed sensors during the production process. This initial calibration ensures that the speed readings are within an acceptable range before the treadmills are shipped to customers. However, it is still recommended to perform regular calibration to account for any changes or discrepancies that may occur over time.
Calibration techniques may vary depending on the treadmill model and manufacturer. It is important to refer to the treadmill’s user manual or consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific calibration instructions and recommendations.
Factors Affecting Sensor Accuracy
Several factors can impact the accuracy and reliability of treadmill speed sensors. These factors need to be considered during calibration and regular maintenance to ensure optimal sensor performance. Here are some of the key factors:
-
Belt Tension: Improper belt tension can affect the accuracy of speed readings. If the belt is too loose or too tight, it may cause slippage or drag, leading to inaccurate speed measurements. Regularly adjusting and maintaining the proper belt tension is crucial for sensor accuracy.
-
Belt Alignment: The alignment of the treadmill belt can influence the speed sensor’s performance. If the belt is misaligned, it may cause uneven or erratic speed readings. Regularly adjusting and aligning the belt ensures that it moves smoothly and consistently.
-
Sensor Positioning: The position of the speed sensor relative to the treadmill belt or the user’s movement can affect accuracy. Proper sensor positioning, as recommended by the manufacturer, ensures that the sensor can effectively detect the speed changes and provide accurate readings.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and dust, can impact the performance of speed sensors. Extreme temperature variations or high levels of humidity may affect the sensor’s sensitivity or reliability. Regular cleaning and maintenance, as well as avoiding exposure to extreme conditions, are necessary to minimize the impact of environmental factors.
Regular calibration, adjustments, and maintenance help maintain the accuracy and reliability of treadmill speed sensors. By taking these factors into account, users can ensure that their treadmill provides accurate speed readings, allowing for effective and enjoyable workouts.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance of Treadmill Speed Sensors
Despite the precision and durability of treadmill speed sensors, occasional issues may arise. Troubleshooting and proper maintenance are essential for identifying and resolving these issues, ensuring the continued accuracy and functionality of speed sensors. Here are some common issues, diagnostic steps, and maintenance practices for treadmill speed sensors.
Common Issues with Speed Sensors
-
Erratic Speed Readings: If the speed readings on your treadmill display are inconsistent or fluctuate unpredictably, it may indicate an issue with the speed sensor. This could be caused by factors such as dirt, debris, or misalignment.
-
No Speed Readings: If the treadmill console does not display any speed readings or shows zero speed, it suggests a malfunction in the speed sensor. This could be due to sensor failure, loose wiring, or issues with the control system.
-
Inaccurate Speed Readings: If the displayed speed does not match your actual pace or feels significantly different, it may indicate an accuracy issue with the speed sensor. This could be caused by factors such as incorrect calibration, belt tension problems, or sensor positioning.
Diagnostic Steps for Identifying Sensor Problems
When troubleshooting issues with treadmill speed sensors, it is important to follow a systematic approach to identify and resolve the problem. Here are some diagnostic steps to consider:
-
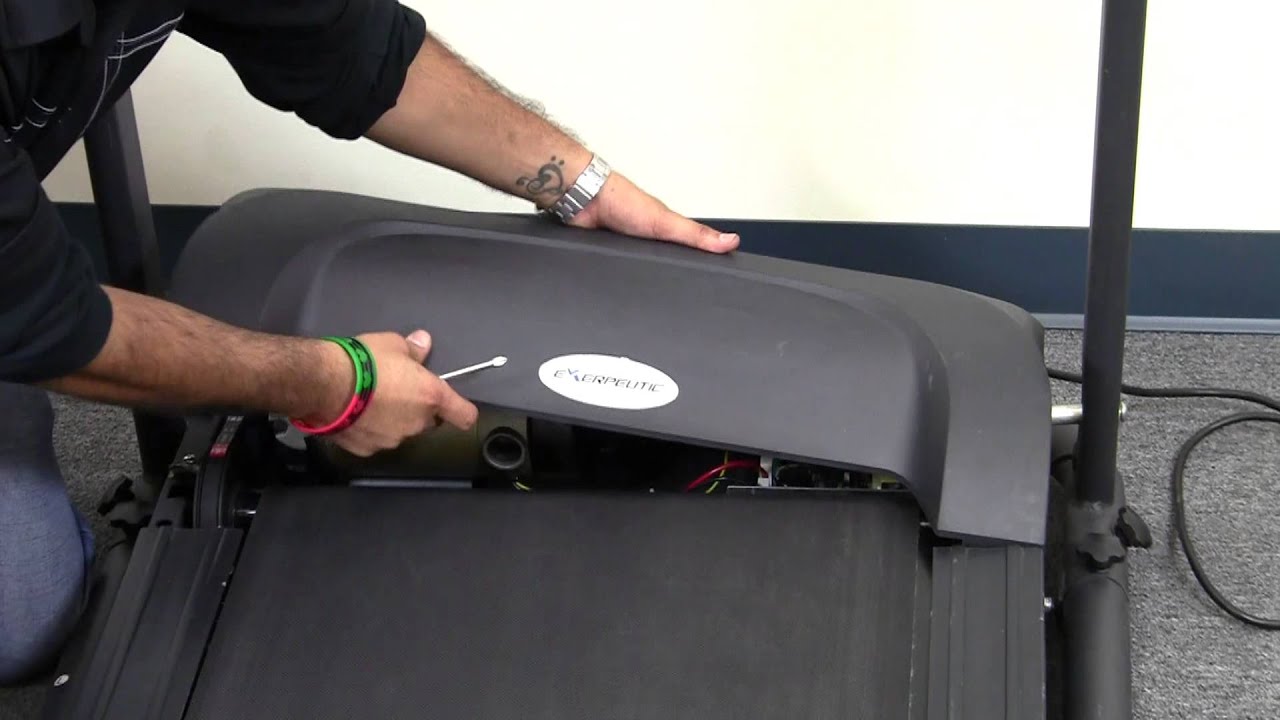
Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the speed sensor, magnets, and wiring for any signs of damage, misalignment, or loose connections. Ensure that no foreign objects are obstructing the sensor’s operation.
-
Cleaning: Clean the sensor, magnets, and reflective surfaces (in the case of optical sensors) using a soft cloth and non-abrasive cleaning solutions. Remove any dirt, dust, or debris that may affect the sensor’s performance.
-
Sensor Realignment: Check the positioning and alignment of the speed sensor. Ensure that it is properly positioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Make any necessary adjustments to correct misalignment.
-
Calibration: If the speed readings are consistently inaccurate, consider calibrating the speed sensor according to the treadmill’s calibration instructions. Follow the recommended calibration techniques to ensure optimal accuracy.
-
Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring connections between the speed sensor and the treadmill’s control system. Ensure that the connections are secure and free from any damage or loose terminals. Tighten any loose connections if necessary.
-
Professional Assistance: If the above steps do not resolve the issue, it may be necessary to seek professional assistance. Contact the treadmill manufacturer’s customer support or a certified technician for further diagnostic and repair.
Proper Cleaning and Care for Sensor Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are critical for ensuring the longevity and accuracy of treadmill speed sensors. Here are some essential practices to keep in mind:
-
Clean the sensor, magnets, and reflective surfaces regularly using a soft cloth and non-abrasive cleaning solutions. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that may damage the sensor or its components.
-
Inspect the sensor, magnets, and wiring periodically for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Repair or replace any damaged parts to maintain optimal performance.
-
Check the alignment and positioning of the speed sensor according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Misalignment or improper positioning can affect the accuracy of speed readings.
-
Monitor the belt tension and alignment to ensure optimal sensor performance. Adjust the belt tension if necessary, following the guidelines provided by the treadmill manufacturer.
-
Consult the treadmill’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for specific maintenance recommendations. Different treadmill models may have unique maintenance requirements, so it is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
By following these maintenance practices and promptly addressing any issues with treadmill speed sensors, users can ensure accurate and reliable speed readings, maximizing their treadmill experience.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Applications and Future Developments of Treadmill Speed Sensors
Treadmill speed sensors have a wide range of applications and play a significant role in enhancing fitness experiences. Let’s explore the various applications of treadmill speed sensors and the potential future developments in this field.
Usage in Treadmill Speed Control Systems
Treadmill speed sensors are integral components of speed control systems in treadmills. These sensors enable the accurate tracking and control of the treadmill’s speed, ensuring that users can maintain their desired pace consistently throughout their workouts. Speed control systems are essential for various training programs, such as interval training, endurance runs, or speed workouts. By incorporating speed feedback from the sensors, the treadmill can automatically adjust the speed based on the user’s requirements, providing a personalized and effective workout experience.
Integration with Fitness Monitoring Devices
Treadmill speed sensors can be integrated with fitness monitoring devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, or smartphone apps. By transmitting speed data to these devices, users can track their treadmill workouts, monitor their speed, distance, and pace, and analyze their performance over time. This integration enhances the user’s ability to set and achieve fitness goals, tailor their workouts based on accurate data, and visualize their progress. Furthermore, fitness enthusiasts can sync their treadmill speed data with other fitness metrics, such as heart rate, calories burned, or elevation gain, providing a comprehensive analysis of their overall fitness journey.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
The field of treadmill speed sensors is continuously evolving, with advancements in sensor technology enhancing their accuracy, reliability, and functionality. Future developments may include:
-
Enhanced Accuracy: Advancements in calibration techniques and signal processing algorithms may lead to even higher accuracy levels in speed measurements. This would further improve the performance and usefulness of treadmill speed sensors.
-
Wireless Connectivity: Integration with wireless connectivity technologies, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, may enable seamless data transfer between the treadmill speed sensor and other devices. This would simplify the process of data synchronization and enhance the user experience.
-
Multi-Sensor Systems: Combining different types of sensors, such as optical and magnetic sensors, in a single system may provide more robust and flexible speed measurement capabilities. Multi-sensor systems could offer enhanced accuracy, redundancy, and resistance to environmental factors.
-
Gesture Recognition: Advanced sensor technologies, such as motion sensors or depth cameras, may enable the recognition of specific gestures or movements on the treadmill. This could enhance the user interface and allow for interactive and immersive workout experiences.
As sensors and technology continue to advance, the applications and capabilities of treadmill speed sensors are likely to expand, providing fitness enthusiasts with new and innovative ways to track, monitor, and improve their treadmill workouts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, treadmill speed sensors are vital components that enable accurate speed measurement, speed control, and performance monitoring in treadmills. Whether using Hall effect technology, magnetic speed sensors, or optical speed sensors, these devices play a crucial role in maintaining consistent speed levels, providing valuable feedback to users, and enhancing overall treadmill performance. Proper calibration, regular maintenance, and troubleshooting practices ensure accuracy and reliability, allowing fitness enthusiasts to make the most of their treadmill workouts. With advancements in sensor technology and integration with fitness monitoring devices, the future of treadmill speed sensors holds exciting prospects for enhanced user experiences and performance evaluation in the fitness industry.

